Is it possible to customize passwords for categories of users? Where and how are passwords managed in SAP?

How can these aspects be checked during an audit?
SAP Password, where do they reside?
In SAP, user passwords, reside in USR02 table. They are stored in BCODE, PASSCODE and PWDSALTEDHASH in an encrypted way. During the various SAP releases the password encryption algorithm has undergone several updates.

In older releases the password is saved in BCODE and PASSCODE fields, in the most recent releases in the PWDSALTEDHASH field.
While in the CODVN field you can view the version of the cryptographic algorithm used by SAP. The field may contain the following values:
- A Code version A (obsolete)
- B Code version B (MD5-based, 8 characters, uppercase, ASCII)
- C Code Version C (Not Implemented)
- D Code version D (MD5-based, 8 characters, uppercase, UTF-8)
- E Code version E (= corrected code version D)
- F Code version F (SHA1, 40 characters, case-sensitive, UTF-8)
- G Code version G = version F + version B (two hash values)
- H Code version H (generic hash method)
- I Code version I = code versions H + F + B (three hash values)
- X Password Deactivated
In the SAP instance profile (visible via RSPFPAR transaction) it is possible, through the parameter login/password_hash_algorithm to verify which is the hashing algorithm in use.
NIST towards minimum measurements
Have you read the NIST sp800-63b publication? NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) is an agency of the government of the United States of America that deals with the management of the technologies.
The obligation to change the password periodically is no longer considered necessary.
- The consequence of requiring password changes is to search for passwords that are easy to remember. Obliges users to remember complicated and difficult password
- The password expiration is not recommended. Password change is required only when there are valid account compromise reasons
- The use of password managers is encouraged
See also here some tips:The Definitive Guide to Passwords in Your Organization
SECPOL as it is thought by SAP
The Security Policy concept was introduced by SAP in the version SAP NetWeaver 7 Enhancement Pack 3 (SAP_BASIS 7.03).
This function can be used for:
- Manage the password structure
- Password's changes
- Manage any logon criteria for specific users
Security policies can be defined through the transaction SECPOL Maintain Security Policies.
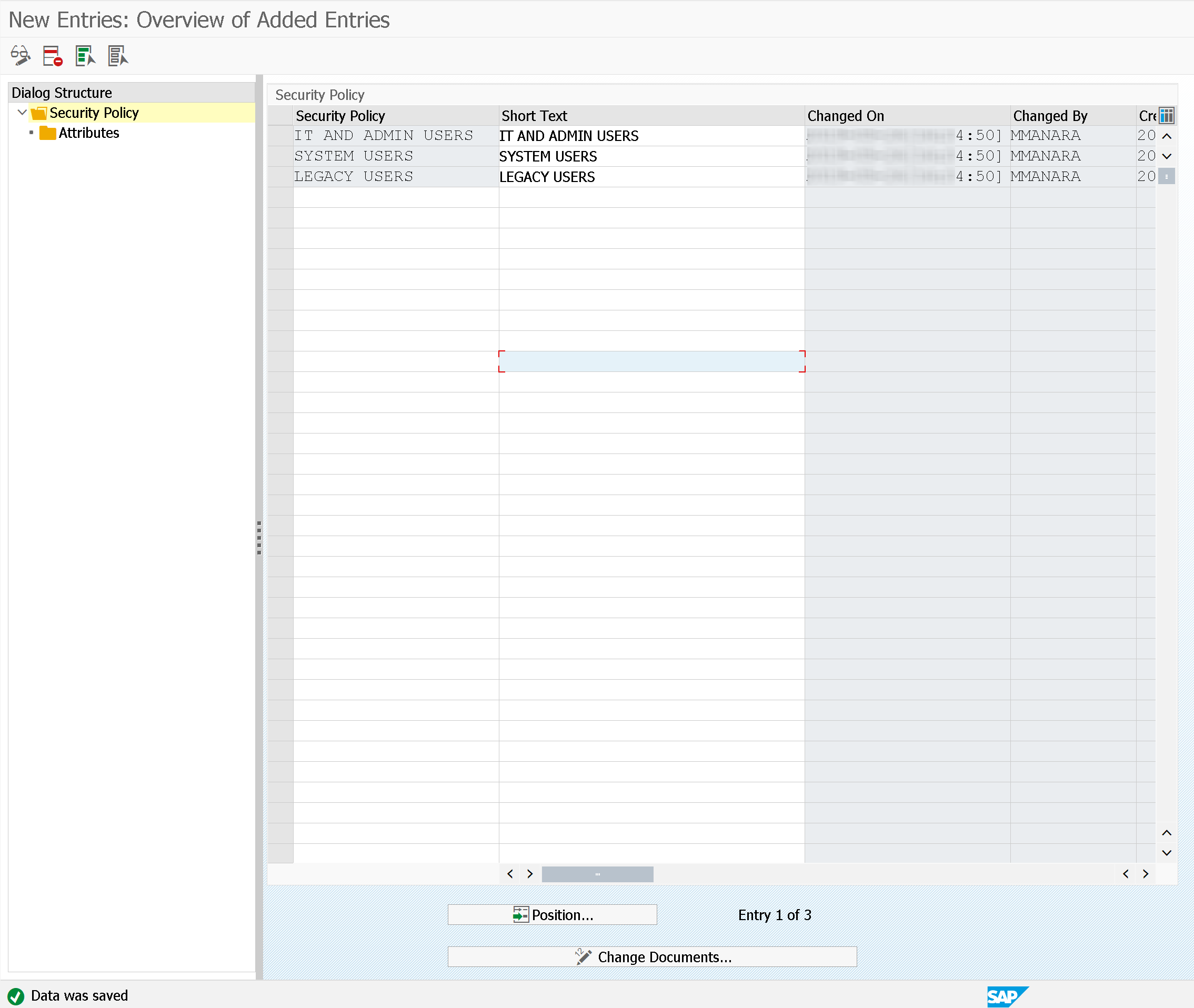
Security policies are a kind of "classification": allow for exceptions to global policies in the system.
Using SAP instance profiles starting with login* (you can see them through the RSPFPAR transaction) you can define how the system should behave when a password is created and selected by an administrator or user.
In some cases, however, it is necessary to have different policies depending on the user. For example, for system administrators the password must be at least 15 characters, while for end users of 10 characters.
Once the classification is defined, in the "Attributes" part you can define the criteria of password complexity defined for that security policy.
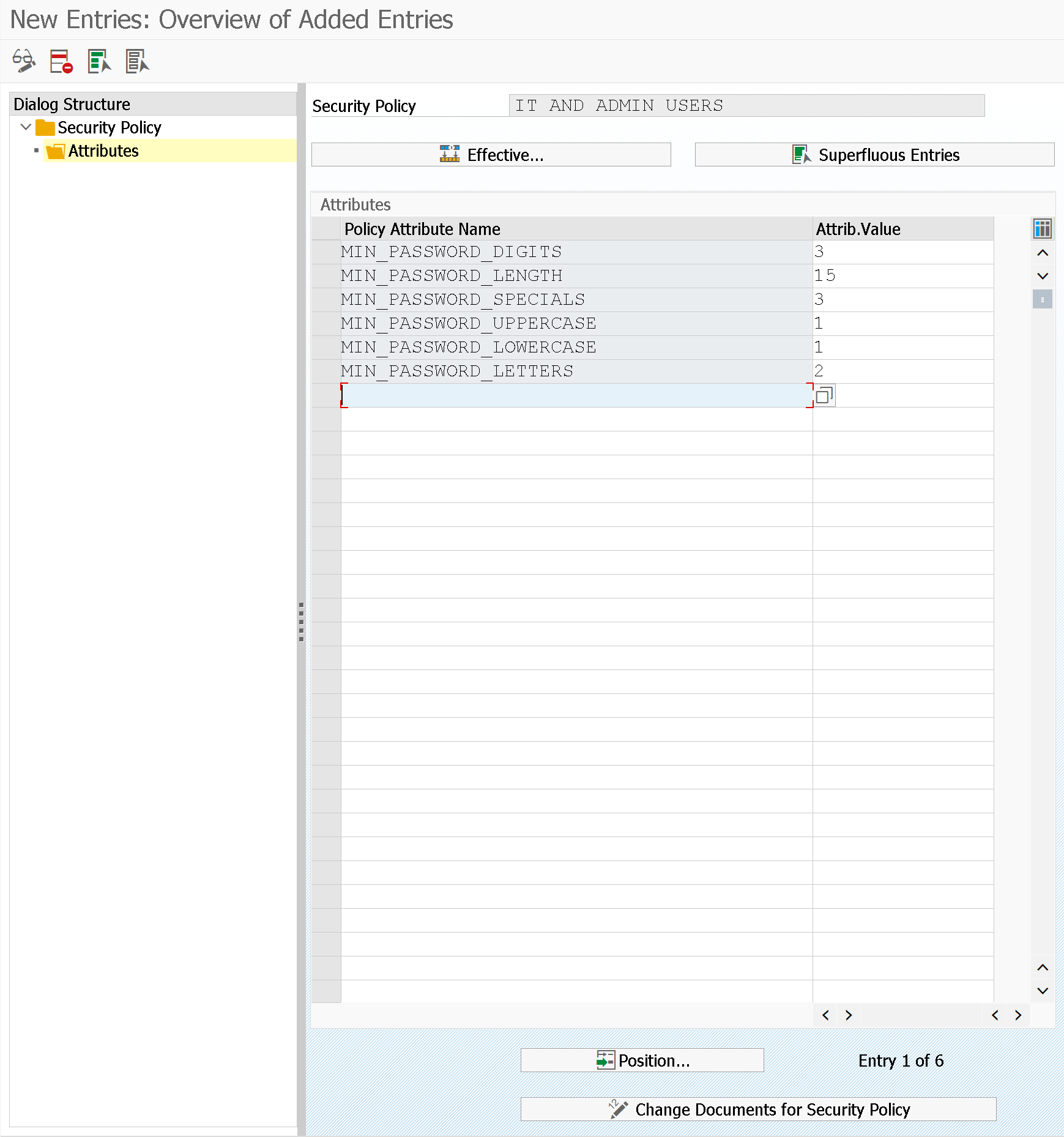
It has been given also the possibility of:
- Select superfluous records, those records that are already contained in the global password policy. For example, if I indicate that the password length is at least 10 characters and in the security policy I indicate the same value, this configuration does not make sense.
- Effective.. the current configuration of the profiles of instance is shown related to passwords in comparison with those of the selected security policy
- All changes to the security policy are traced through a special change document, see Change documents for Security Policy button (through SECPOL_CHANGES transaction)
Once security policies are defined, they must be assigned to users. This is done directly through the SU01 transaction (or similar massive transactions)

Through the S_YI3_39000082 transaction, available also in the transaction SUIM -> Where-Used List -> Security Policies -> Users you can see users with security policy assigned or not.
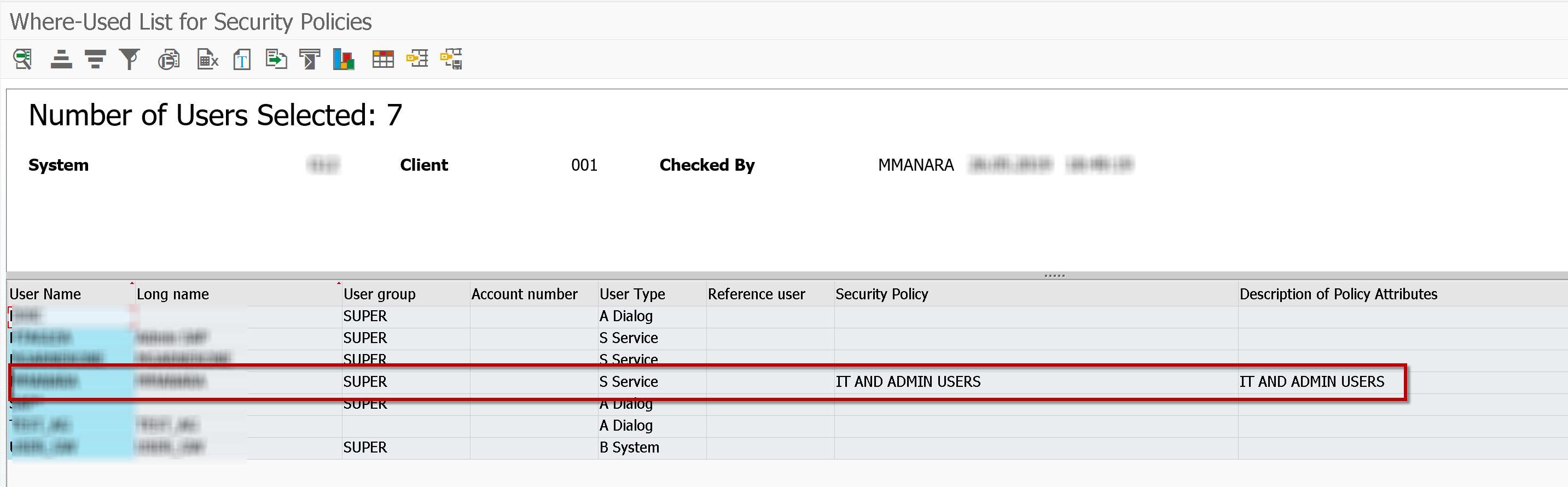
Through the note OSS 2318872 - SU01 field Security Policy is not available in field mapping you can also manage this field in the GRC Access Control Access Request Management.
Security policies can also be used for operational system management aspects. That is, during system maintenance or special times, user groups should not access the system. For example during maintenance, during upgrades or accounting closures.
In the security policy is present an attribute called SERVER_LOGON_PRIVILEGE which allows you to restrict access only to certain users. The parameter can have the following values:
- 0 - No restrictions
- 1 - Only users with security policy applied with value 1 can access the system
- 2 - Users with this value can't access the system (users will receive a message "Server is currently not available (logon not permitted)"
- 3 - External Logon, only who has parameter 3 can access this mode
- 4 - External logon not allowed
External logos are for example RFC destinations. The relative profile of instance is as follows: login/server_logon_restriction see also OSS note (1891583 - Restricting logon to the application server)
Don't forget SAP special users
SAP uses special utilities for some purposes, these utilities have public and known passwords, here are:
- SAP*
- DDIC
- SAPCPIC
- EARLYWATCH
- TMSADM
Blog post originally translated from: https://www.aglea.com/blog/sap-password-policy
